Hot News Today
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Tulongan po natin sya.
Sa aking pagreresearch sa sakin na ito, ito po ay.
Spinal Muscular Atrophy
What is spinal muscular atrophy?
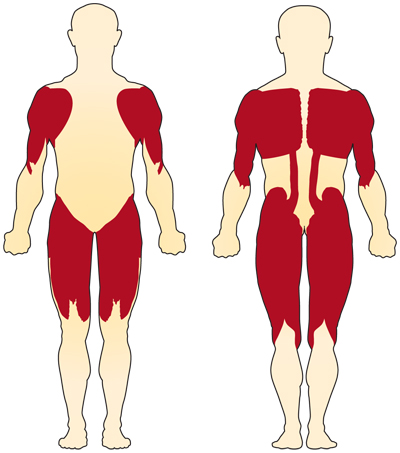
The muscles closer to the center of the body (proximal muscles) are usually more affected in spinal muscular atrophy than are the muscles farther from the center (distal muscles).
Most of the nerve cells that control muscles are located in the spinal cord, which accounts for the word spinal in the name of the disease. SMA is muscular because its primary effect is on muscles, which don’t receive signals from these nerve cells. Atrophy is the medical term for getting smaller, which is what generally happens to muscles when they’re not active.
SMA involves the loss of nerve cells called motor neurons in the spinal cord and is classified as a motor neuron disease.
In the most common form of SMA (chromosome 5 SMA, or SMN-related SMA), there is wide variability in age of onset, symptoms and rate of progression. In order to account for these differences, the chromosome 5 SMA often is classified into types 1 through 4.
The age at which SMA symptoms begin roughly correlates with the degree to which motor function is affected: The earlier the age of onset, the greater the impact on motor function. Children who display symptoms at birth or in infancy typically have the lowest level of functioning (type 1). SMA onset in children (types 2 and 3), teens or adults (type 4) generally correlates with increasingly higher levels of motor function.
Ano Po opinion ninyo?
please share.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps